Master AQL (Acceptance Quality Level) for Garment Marnufacturting
A vital component of any production process, quality control is especially significant in the fashion manufacturing sector. great-end apparel and accessories that not only look good but also last over time are in great demand from both brands and customers.
Vinmake, a B2B platform for fashion production for international brands, is aware of how important it is to uphold strict quality control standards in order to satisfy customers and satisfy their requests. This essay will examine AQL (Acceptance Quality Level), a crucial quality control standard in the garment manufacturing sector.
Comprehending AQL
AQL (Acceptance Quality Limit or Acceptable Quality Level) is the acceptable quality threshold—a standard used by many businesses to randomly inspect a sample of products from a lot to assess the risk of defective goods. This quality control method was developed by Motorola, Inc. in 1986.
Read more about the AQL (Acceptance Quality Limit) ?
The Operation of AQL
AQL Level Setting:
Manufacturers define distinct AQL levels for various defect categories based on client needs and the criticality of the product.
For instance, a lower AQL level is required for serious flaws like broken zippers or improper size, whereas a higher AQL level can be appropriate for minor flaws like loose threads.Sampling at Random:
Products are selected at random from a production lot.
The AQL level and the required degree of confidence are used to calculate the sample size.Examination:
The products that were sampled are examined for flaws.
The AQL level is contrasted with the quantity of flaws discovered.Making Decisions:
The entire lot is approved if the sample's defect count is less than the AQL.
The lot can be rejected or more inspections or remedial measures might be needed if the quantity of flaws above the AQL.
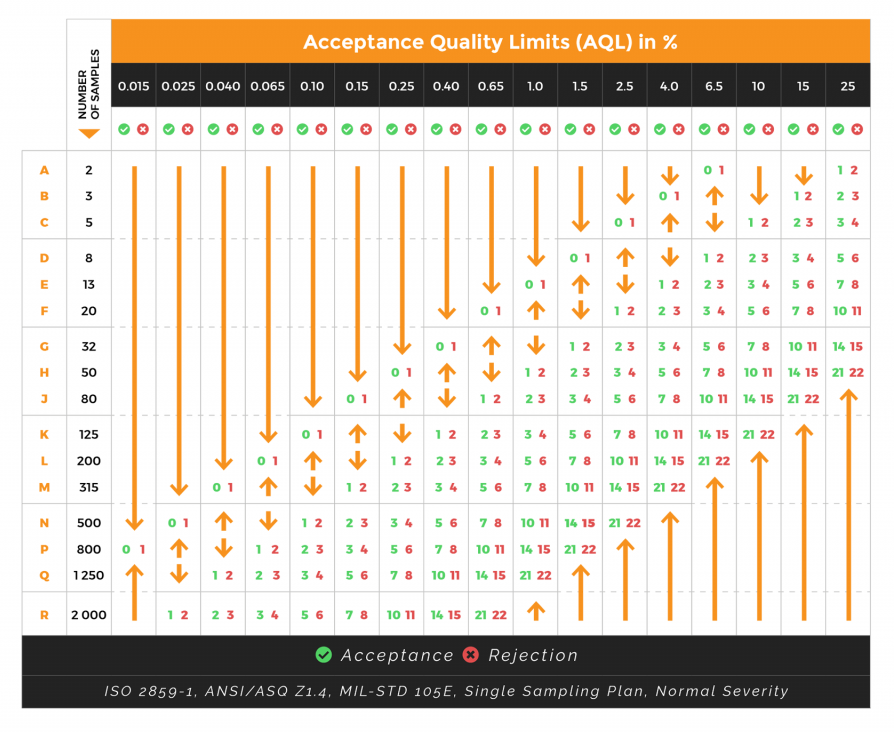
The AQL table (or AQL chart) is part of ISO 2859, designed to guide users in determining two key factors:
How many samples need to be inspected in a product lot.
The threshold between accepting and rejecting defective products.
The AQL chart consists of two tables:
Table 1: Used to determine the sample size code based on the lot size and inspection level by identifying the intersection of the corresponding row and column.
AQL Table 1
For example, a company has a lot of 5,000 shirts to be stitched, and the required AQL level is GII. The sample size code, as specified in the table, is located at the intersection of the lot size row and the inspection level column. As shown in the table below, the inspection level is “L.”
Table 2: Used to determine the appropriate sample size, select the AQL standard, and make decisions based on thresholds provided by the chart. These thresholds are similarly identified at the intersection of the inspection level row and the AQL column.
Classification of AQL Defects by Severity
In practice, there are three common types of AQL defects:
AQL 0% for critical defects: These are completely unacceptable as they may cause harm to users, violate regulations, or lead to catastrophic economic impacts.
AQL 2.5% for major defects: These products are generally deemed unacceptable by end-users, such as items that do not function as intended.
AQL 4.0% for minor defects: These involve slight deviations from specifications, posing only minor inconveniences that most users would either not notice or not mind.
Related Concepts:
RQL (Rejectable Quality Level): The level of quality deemed unacceptable.
IQL (Indifference Quality Level): A quality level that falls between AQL and RQL, typically agreed upon between buyers and sellers to represent an acceptable AQL level reflecting the risk assumed by each party. It is used as a reference during pre-shipment inspections.
Advantages of AQL Use
Better Product Quality: Manufacturers can guarantee that products fulfill particular quality requirements by establishing and implementing AQL standards.
Increased Customer Satisfaction: Happy consumers and repeat business are the results of high-quality items.
Lower Costs: By detecting and fixing quality problems early in the production process, AQL helps avoid expensive recalls and rework.
Effective Quality Control: AQL offers a methodical approach to quality control that makes inspection and decision-making more effective.
Industry Standards Compliance: To guarantee adherence to industry rules, AQL is frequently used in combination with other quality standards, including ISO 9001.
Important Factors for Successful AQL Implementation
Clear AQL Standards: Create precise and unambiguous AQL standards for various product kinds and defect classifications.
Trained Inspectors: Verify that inspectors have received the necessary training to reliably and precisely identify flaws.
Frequent Monitoring and Review: To adjust to evolving customer needs and manufacturing procedures, monitor AQL performance on a regular basis and review standards as necessary.
Effective Communication: Share AQL expectations and standards with all parties involved, such as manufacturing teams, suppliers, and quality control staff.
Continuous Improvement: By putting preventative and corrective measures in place, continuously work to enhance AQL performance.
Conclusion
Clothing manufacturers can greatly improve product quality, lower faults, and establish a solid reputation for providing their clients with high-quality items by successfully implementing AQL.
Acceptable Quality Limit (AQL) Calculator
Looking for producing garment in Vietnam?